女性の半数、危険な性交渉? 抗生物質で治らない「スーパー淋病」が英国で感染流行か!
2016.05.11
イギリスのウェスト・ミッドランド地域北西部、および南西部で相次いで淋菌の新株が発見さている。この進化した淋菌は、抗生物質に対しての抵抗力が非常に強く、2014年に最初の感染者が見つかってから34人の感染者が確認されており、専門家たちからの警鐘が鳴らされている。
■抗生物質に対して強い耐性を持つスーパー淋菌が出現
イギリスの「Daily Mail」紙のレポートによれば、このスーパー淋菌によって発症する新型淋病に対して、現時点では有効な治療手段がなく、大規模な感染流行の危険性が潜んでいるとのことである。
確認されている患者は、ウェスト・ヨークシャー、ウェスト・ミッドランド、ロンドンの北部と南部と地域的に限定されてはいるが、まだ確認されていない患者やキャリア(感染者)は多数いるのではないかと想定される。おそらく女性の半数と男性の10人に1人は感染に気がつかないまま、感染源として危険な性交渉をしているのではないかと疑われている。
このスーパー淋菌は、抗生物質に対して非常に強い耐性を持ち、現時点で淋菌に対して有効とされている2つの抗生物質のうち、ひとつには完全な耐性を持っていて、もうひとつに対しても非常に早い速度で進化し耐性をつくりあげる過程にあるという。通常の淋病の治療で使用される2種類の抗生物質のひとつ、アジスロマイシンに対しては完全耐性があり、もうひとつのセフトリアキソンに対しては部分耐性があるという状況なのだ。

淋病は、すぐに直接死に結びつく性感染症ではないが、治療が遅れたり、このスーパー淋病のように薬が効かなかったりすれば、不妊や流産の原因となったり、視力に障害をもたらしたり、重篤な炎症を引き起こすこともあり、当然のことながら適切な治療が必要な感染症である。イギリス保健省のチーフメディカルオフィサーのダム・サリー・デイヴィス教授は、このスーパー淋菌に対して、昨年の12月には「もはや淋病は治療不可能な病気になる危険がある」と国内の医療関係者に警告文書を発信しており、また、保健省当局から公に不用意なカジュアルセックスを控えることと、新しいパートナーとのセックスの際にはコンドームの使用を促すという警告も出されている。
■医療の進歩がウイルスを強く凶悪なものへと進化させている
このスーパー性病を引き起こす新株は、昨今医学界、薬学界でなにかと話題にのぼる薬剤耐性を持つ微生物、特に抗生物質耐性微生物が多数出現している事態を表すひとつの例であり、医師や薬剤師による、薬の過剰な処方による結果でもあるとされている。ある例をあげれば、ペニシリンなどの数種類の抗生物質は、いまでは皮膚の感染症や、のどの痛み、肺炎には効き目がなくなってきているという。
デイヴィス教授によれば「抗生物質に耐性がある微生物の脅威は、テロリズムと同等の危険性がある。ちょっとした切り傷でも、そこから耐性菌が侵入してしまう可能性もある。」とのこと。また、ジョージ・オズボーン財務大臣は、抗生物質耐性菌は2050年までに、年間のガンによる死者数を超え、年間一千万人超の死者を出すことになるであろうと発言している。

なんでも薬で治ってしまうという“薬神話”があるが、医師や薬剤師が薬を過剰に使用していることだけでなく、患者自身もまた多くの薬の処方を望んでいる事実もあるのだろう。抗生物質の発見は、おそらく医療界での革命だったに違いないが、それが微生物をさらに強く凶悪なものに進化させてしまったとも言えるだろう。医学の進歩か微生物の進化か、どちらが勝つかはわからないが、不用意なセックスはしばらく避けたほうがよさそうである。
(文=高夏五道)
参考:「Daily Mail」ほか
参照元 : TOCANA
Sex superbug that is sweeping the country: Experts' worry over gonorrhoea strain that's becoming immune to antibiotics
・New strain found in the West Midlands, north and south east of England
・It has been found to be highly resistant to drug antibiotic azithromycin
・There have been 34 confirmed cases since November 2014
By HARVEY DAY FOR MAILONLINE
PUBLISHED: 13:47 GMT, 17 April 2016 | UPDATED: 11:59 GMT, 21 April 2016
A sexually transmitted ‘superbug’ that is on the verge of becoming untreatable is sweeping across Britain, health experts warn.
Cases of the drug-resistant gonorrhoea strain have been confirmed in West Yorkshire, the West Midlands, London and the North East.
But there are likely to be many others which have gone unreported, officials fear. It is caused by a bacteria quickly becoming immune to one of the last two available antibiotics. Experts fear it will soon develop a resistance to the second drug – and there are no others in reserve. Health officials are urging the public to limit casual sex and wear condoms with a new partner.
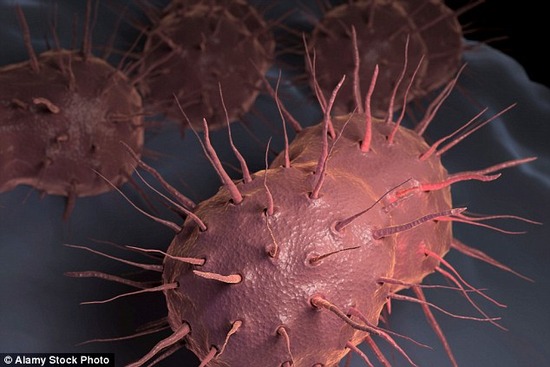
A highly drug-resistant type of 'super-gonorrhoea' is spreading across the country, with senior medics warning it may become untreatable. Neisseria gonorrhoeae (above), the bacterium responsible for the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea
GPs have also been warned to be extra vigilant and ensure they prescribe the proper treatment. But the spread of this ‘super’ sexually transmitted disease is further evidence of the growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bugs. For decades, antibiotics have been so overused by GPs and hospital staff that the bacteria have evolved to become resistant. Doctors report that medicines including penicillin no longer work on sore throats, skin infections and more seriously, pneumonia.
Chief Medical Officer Dame Sally Davies has said the threat is as severe as terrorism – with patients dying from minor cuts after succumbing to drug-resistant bugs. And only last week Chancellor George Osborne said that antibiotic-resistant bacteria will claim ten million deaths a year worldwide by 2050 – even more than cancer.
Public Health England yesterday issued an alert stating that cases of this super-gonorrhoea were continuing to rise and represented a ‘very real threat’.
So far 34 adults have been diagnosed with the strain since November 2014 but this is almost certainly only the tip of the iceberg. More than half of women and one in ten men never see symptoms so may pass on the infection unaware.
But they are at risk of serious complications and untreated, the disease can cause infertility or inflammation of the womb. It is particularly dangerous for pregnant women and may lead to miscarriage, premature labour or sight problems in the baby. Usually gonorrhoea is treated with a jab, known as ceftriaxone, then by a pill called azithromycin. But this strain is already partly resistant to the latter and experts are worried it will soon also become immune to the former. Dr Gwenda Hughes, of PHE, the Government body in charge of preventing the spread of bugs, said: ‘We cannot afford to be complacent.
The strain is 'highly resistant' to the antibiotic azithromycin, meaning medics are relying on a second drug, ceftriaxone, to treat it. Above an image of gonorrhea
‘If strains of gonorrhoea emerge that are resistant to both azithromycin and ceftriaxone, treatment options would be limited as there is no new antibiotic available.’ Dr Elizabeth Carlin, president of the British Association of Sexual Health and HIV, said: ‘The fact that we have resistance developing to one of the drugs we use means that we could potentially be left with only one drug to use. If it becomes resistant to that, we would be in a very difficult position.’ Doctors are also worried as the strain is now being reported in gay men so may start spreading even more quickly. Dr Peter Greenhouse, a consultant in sexual health based in Bristol, said: ‘The problem is [they] tend to spread infections a lot faster simply as they change partners more quickly.’ In December, Dame Sally Davies wrote to GPs and pharmacists in December warning them that ‘gonorrhoea was at risk of becoming an untreatable disease’. She reminded them to ensure they prescribed both the ceftriaxone jab and the azithromycin pill – some were omitting the injections. Gonorrhoea is the second most common STD after chlamydia and is spread through unprotected sex. Annual cases have risen by a fifth, and some experts link this to a rise in casual sex. There were 34,958 confirmed infections in England during 2014, most commonly in the under-25s, up from 29,419 the previous year. Officials at PHE have tried to contact all sexual partners of anyone diagnosed with the superbug but have only managed to find 22 of the 50 partners. More than 90 per cent of those they did track down were confirmed as having the infection. This means there is a high chance the other adults also had it and may have passed it on.
If untreated, gonorrhoea can result in severe complications and lead to infertility or septicaemia in rare cases
GONORRHOEA: EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE DISEASE
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria called Neisseria gonorrhoeae or gonococcus.
The bacteria can infect the cervix (entrance to the womb), the urethra (tube through which urine passes out of the body), the rectum and less commonly the throat or eyes. The infection can also be passed from a pregnant woman to her baby. If you are pregnant and may have gonorrhoea, it is important to get tested and treated before your baby is born.
Without treatment, gonorrhoea can cause permanent blindness in a newborn baby. Gonorrhoea is usually treated with a single antibiotic injection and a single antibiotic tablet. With effective treatment, most of your symptoms should improve within a few days. It is usually recommended that you attend a follow-up appointment a week or two after treatment, so another test can be carried out to see if you are clear of infection. Anyone who is sexually active can catch gonorrhoea, especially people who change partners frequently or do not use a barrier method of contraception, such as a condom, when having sex. Gonorrhoea is the second most common bacterial STI in the UK after chlamydia. Almost 35,000 cases were reported in England during 2014, with most cases affecting young men and women under the age of 25. Previous successful treatment for gonorrhoea doesn't make you immune to catching the infection again.
Source: NHS
参照元 : Daily Mail
抗生物質効かないスーパー淋病 日本の風俗店の女性から発見
2014.05.22 16:00

世界保健機関(WHO)がいま、世界的な蔓延を警告する病気、それが「淋病」である。
「終末論的な幻想ではないが、一般的な感染症や軽傷が致死的となるポスト抗生物質時代が21世紀に到来する可能性は非常に高い」
「抗生物質の開発や生産、処方の方法を変えなければ、世界は公衆衛生の実現手段を失い、その影響は壊滅的になる」
WHOのケイジ・フクダ事務局長補は記者会見でこう述べた。
「終末論的な幻想」「影響は壊滅的」……およそ国連機関の幹部の言葉とは思えないおどろおどろしい文言だが、それが大げさではない状況にある。
この4月30日に発表された「抗菌薬耐性:2014年世界報告」は254ページにわたり、従来の抗生物質では死滅しない「超強力な細菌(スーパーバグ)」に関する調査結果や医療の状況などについて報告した。それによれば、世界の国々で抗生物質が効かない耐性を持った黄色ブドウ球菌や大腸菌などが出現し、警告レベルに達しているという。
いままで抗生剤を飲んでいれば治っていた結核、大腸炎、肺炎などの感染症が“不治の病”に逆戻りする。江戸時代のコレラの大流行を描いたTVドラマ『JIN―仁―』(TBS系)のように、150年前と同じ深刻な状況が再び訪れる可能性があるのだ。
淋病研究の権威で、元・産業医科大副学長の松本哲朗氏(現・北九州市役所保健福祉局医務監)はいう。
「淋病に抗生物質が効かなくなりつつあります。最初はペニシリンが効かない耐性菌ができ、それ以降、さまざまな抗生物質が開発されては効かなくなった。日本においてセフィキシムは、決められている投与量では効く人と効かない人が半々という状況なので、現在は注射剤のセフトリアキソンという抗生剤が主に使われています。
しかし、このセフトリアキソンも、4年前に日本で完全に耐性をもつ菌が発見され、世界の医療関係者に衝撃が走ったのです」
「最後の切り札」ともいえるセフトリアキソンにも耐性をもつ「スーパー淋病」がすでに誕生しているのである。しかも、世界で初めてこのスーパー淋病が発見されたのは日本だった。
その耐性菌を発見したのが、保科医院(京都市)の保科眞二医師である。
「京都市内のファッションヘルスに勤める女性(当時31歳)の定期検診で、咽が淋菌に感染していることがわかり、セフトリアキソンを投与したところ、菌が消えなかったのです。
それで菌を採取したのち、もう一度、投与したところ、菌が消えた。ただ、咽頭淋菌は、当医院の調査によると25%は自然になくなっていくので、抗生剤が効いたのか、自然になくなったのかは定かではありません」
採取した淋菌を解析したところ、セフトリアキソンに対する非常に強い耐性をもっていることが判明したのだ。世界にショックを与えた、スーパー淋病発見の瞬間である。
日本で確認されているスーパー淋病の事例は、今のところ京都の1件のみだが、海外ではヨーロッパとオーストラリアで発見され、増加しつつある。もちろん、日本は1件だけだから安心だとはいえない。
「女性の場合、症状が出にくいので、他で耐性菌が生まれ、感染に気づかないままもっている人がいるという可能性は考えられます。それが広がらないかどうか、心配されるところです」
松本氏はそう警告する。海外で性的な接触をした人が日本に持ち込んでしまったり、海外の保菌者が日本に旅行に来て持ち込む可能性も十分にあるのだ。
スーパー淋病に効く新たな抗生物質の開発が望まれるが、「今のところ、セフトリアキソンにかわる有効で使いやすい抗生剤は存在しない。製薬会社や国の研究機関も含めて、新しい抗生物質の開発スピードが鈍っているというのが厳しい現実」(松本氏)だという。
耐性菌と新薬のイタチごっこはこれまでずっと続いてきたが、いよいよ限界。そのためWHOも異例の警告に踏み切ったのだ。
※週刊ポスト2014年5月30日号
参照元 : NEWSポストセブン
昨日便座からスーパー淋病感染の話聞いたから会社のトイレ怖いんだけど…
— RiND40 (@RiND40) 2016年5月17日